Reducing methane emissions from animal manure
In today’s world, the urgency to address climate change has magnified the need to mitigate the harmful effects of methane gas. This greenhouse gas possesses a significantly greater warming potential than carbon dioxide, propelling researchers and innovators to explore sustainable alternatives. One such solution gaining momentum is the conversion of methane from animal manure into biogas. This article dives into the various facets of this technology, encompassing its environmental impact, economic viability, and global feasibility.
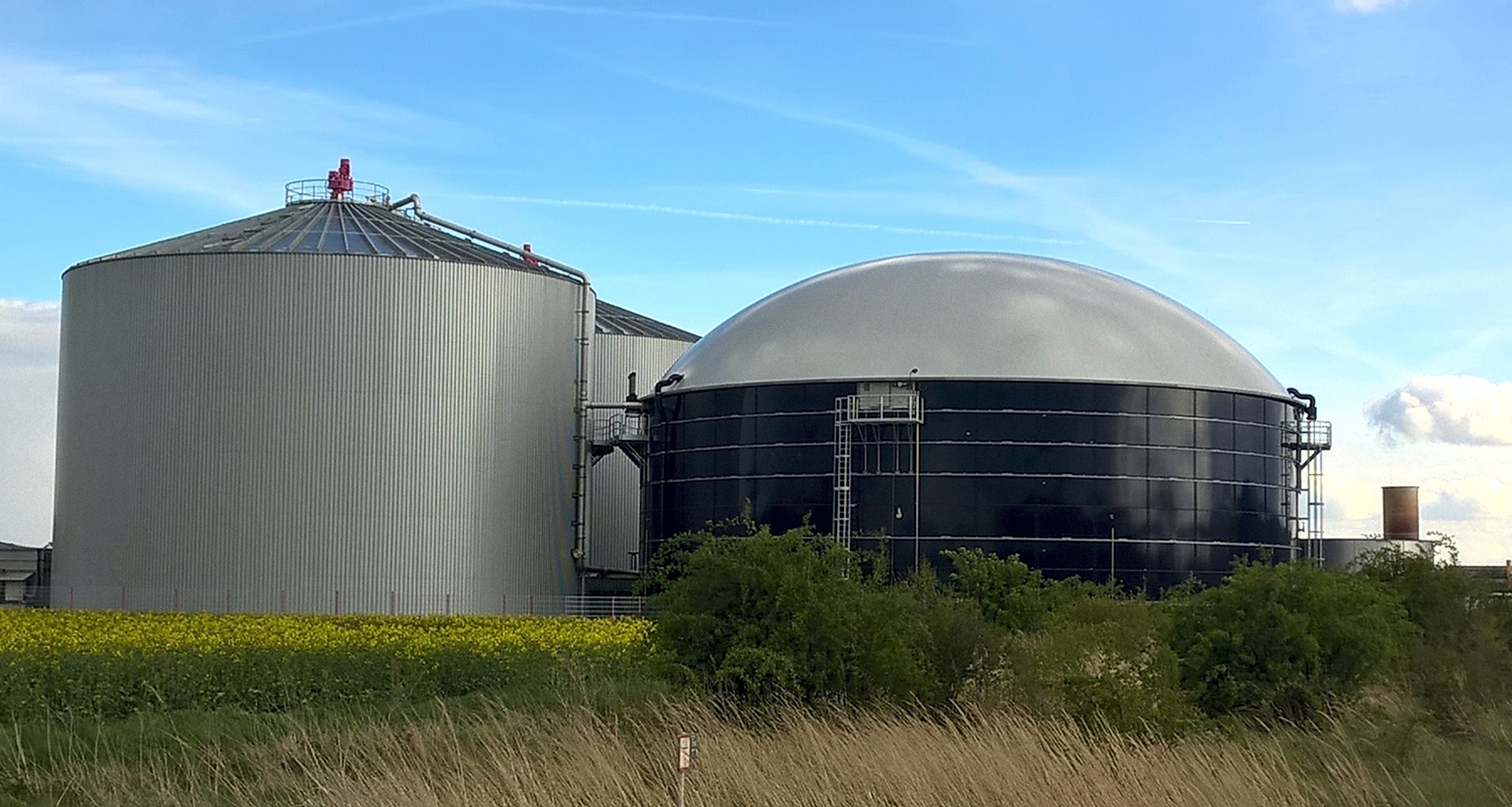
Several CO2-projects are focusing on this process. They supply biodigesters to rural households and farms, which oftentimes are not connected to a power grid or sewage system.
By engaging in biogas projects, companies can buy carbon credits to further support their commitment to sustainability and contribute to achieving net-zero emissions goals.
The methane conversion process
The conversion of methane from animal manure into biogas involves a sequence of biological and chemical reactions. Vital to this process are biodigesters, varying from fixed dome to composite types, which enable anaerobic digestion. Within subterranean chambers, organic waste, like cow dung, undergoes digestion, giving rise to methane-rich biogas. Through outlet chambers, the predominant methane biogas is captured and transferred into kitchen stoves (for cooking), while the remaining slurry proves valuable as an organic fertilizer (reducing the need to buy fertilizer).
Environmental and social benefits are plentiful
- Mitigating climate change: Directly reducing harmful greenhouse gas emissions, the conversion of methane into biogas establishes cleaner indoor environments by substituting conventional fossil fuels for household cooking and heating.
- Deforestation and resource preservation: The replacement of unsustainable biomass fuels with biogas curbs deforestation and lessens the use of finite resources, such as firewood.
- Enhanced sanitation: Beyond efficient waste management on farms, this technology facilitates connections between latrines and sewers or biogas digesters, resulting in healthier living conditions.
- Improving water quality: By preventing untreated manure discharge into surface waters, the strain on water bodies diminishes, contributing to the preservation of water quality.
Economic considerations
- Leveraging carbon credits: Many projects are not state funded and rely on revenue from carbon credits. This further encourages greenhouse gas emission reductions and fosters sustainable practices. Companies can buy carbon credits and therefore directly fund these projects.
- Energy efficiency: Households reap savings on domestic thermal energy expenditures, as biogas displaces conventional fossil fuels.
- Boosting agricultural output: The application of bio-slurry as organic fertilizer trims costs related to (synthetic) fertilizers and can augment agricultural yields.
Global implementation at scale
While the technology displays promise, its wide-scale adoption encounters both opportunities and challenges. Instances of successful global implementation abound, with projects installing numerous biodigesters, numbering from hundreds of thousands to millions per project. Some obstacles to overcome are the initial infrastructure and technology costs, limited awareness, insufficient technical knowledge, and inadequate sources of appropriate waste pose challenges. This is the mission of dedicated project developers, which specialize in deploying digesters and training local workers to operate and maintain these machines.
Conclusion: should you buy carbon credits to reduce methane emissions?
The conversion of methane from animal manure into biogas unveils a promising path for mitigating methane emissions, advancing energy sustainability, and elevating agricultural practices. Yet, successful implementation hinges on factors such as economic viability, policy endorsement, and public awareness. As the world grapples with climate change, embracing this technology could propel us towards a cleaner, more sustainable future.
By championing the conversion of methane from animal manure into biogas, companies wield the power to combat climate change, diminish greenhouse gas emissions, and foster sustainable practices. The responsibility rests with Heads of Sustainability and ESG leaders to spearhead transformative change on a global scale.
Companies can contribute to achieving net-zero emissions by actively participating in biogas initiatives and purchasing carbon credits, solidifying their commitment to environmental stewardship and a sustainable world.
Reach out to us to learn more about these projects and carbon credits.